Describe the Technique Used to Create a Recombinant Dna Plasmid
Mix DNA they join by base pairing 4. Molecular cloning is the laboratory process used to create recombinant DNA.
Recombinant Dna Biological Principles
After a ligation the next step is to transfer the DNA into bacteria in a process called transformation.

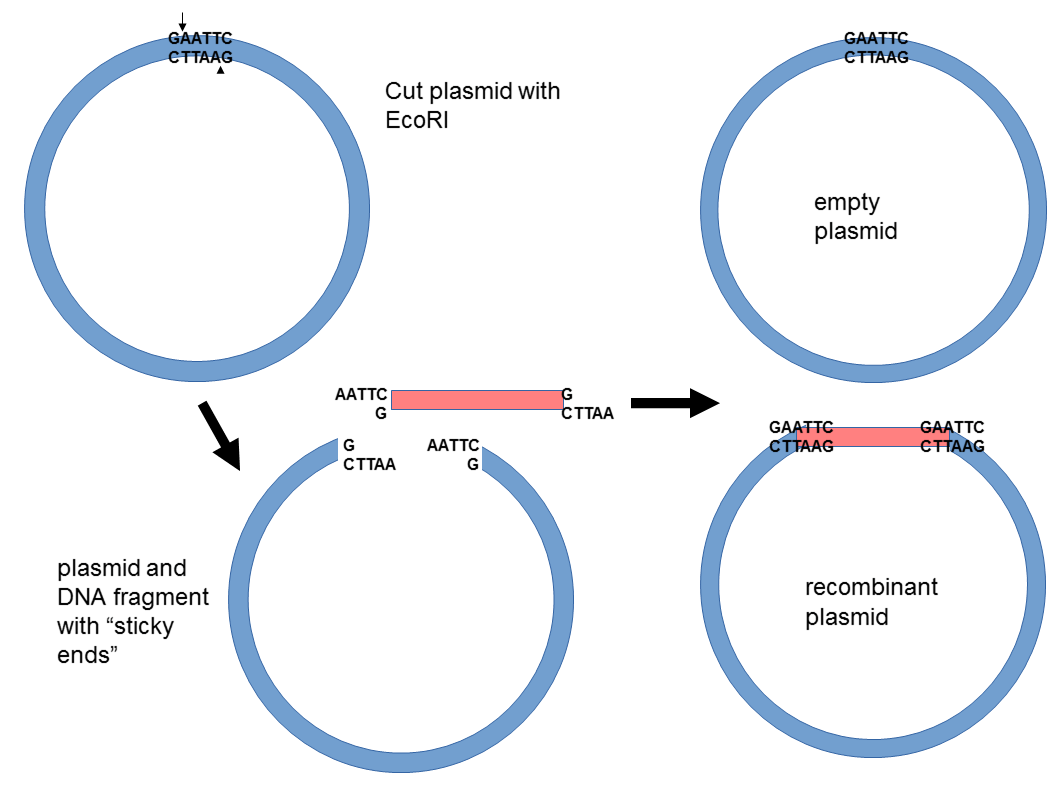
. Cut a circular bacterial plasmid to make it linear 3. Recombinant DNA technology refers to the joining together of DNA molecules from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science medicine agriculture and industry. Insert the genomic DNA fragments into the plasmid to make recombinant DNA molecules.
Recombinant DNA technology is used in a wide range of applications from vaccine production to the production of genetically engineered crops. The next step in the cloning process is to cut the vector with the same restriction enzyme used to cut the donor DNA. During recombinant DNA technology a fragment of DNA can be cut out and inserted into a vector.
The cohesive ends of vector DNA possess the sequences of nucleotides complementary to the cohesive ends of foreign DNA. The restriction enzymes utilized in recombinant DNA technology are significant to detect the location at which the desired gene is introduced into the vector genome. Thus it is a type of DNA that would be impossible naturally and is an artifact created by DNA technology.
Recombinant DNA is a technology scientists developed that made it possible to insert a human gene into the genetic material of a common bacterium. Probe is used to isolate the gene of interest 2 Enzymatically cleave DNA into fragments. The recombinant DNA technology emerged with the discovery of restriction enzymes in the year 1968 by Swiss microbiologist Werner Arber Inserting the desired gene into the genome of the host is not as easy as it sounds.
The whole process is known as molecular cloning. The isolated and purified DNA is treated with restriction endonucleases which cut the DNA into fragments. Joining together of DNA fragments from different sources creates recombinant DNA.
The restriction enzyme which causes a break in foreign DNA also causes a staggered cut in the vector DNA at a specific cleavage site. The genes may be from one organism or several. The resulting molecule is called recombinant DNA.
Techniques of recombinant DNA technology gene therapy and genetic modifications are also widely used for the purpose of bioremediation and treating serious diseases. The use of the word clone has been extended to recombinant DNA technology which has provided scientists with the ability to produce many copies of a single fragment of DNA such as a gene creating identical copies that constitute a DNA clone. Molecular cloning is shown in figure 2.
The cloned DNA segment may be replicated within a cell using recombinant DNA technology or in a test tube using the polymerase chain reaction PCR. Chemical method or Maxam-Gilbert Method. Isolate DNA from two sources 2.
As the bacteria grows and divides the recombinant plasmids replicate thereby amplifying the. Recombinant DNA requires 3 key molecular tools. It is one of two most widely used methods along with polymerase chain reaction PCR used to direct the replication of any specific DNA sequence chosen by the experimentalist.
It involves the selection of the desired gene for administration into the host followed by a selection of the perfect vector with which the. Each bacterium receives a different plasmid. Recombinant DNA is an important technique for many gene-cloning applications.
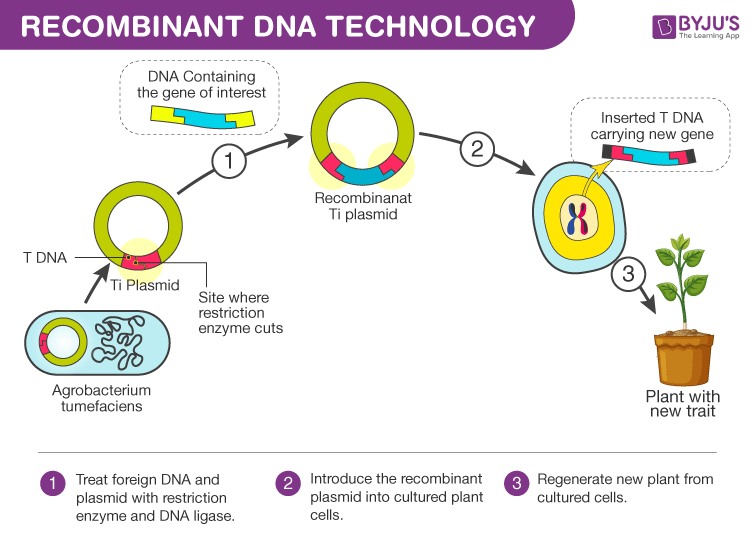
Recombinant DNA technology combines DNA from different sources to create a different sequence of DNA. In a typical cloning experiment researchers first insert a piece of DNA such as a gene into a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid. May 19 2021 by Sagar Aryal.
Molecular Cloning and Recombinant DNA Technology. The ability to cut and paste DNA might seem like purely a technical feat but one key application that arose out of this is molecular cloning. The methods commonly used for DNA sequencing are.
Recombinant DNA rDNA on the other hand is the general name for a piece of DNA. Scientists build the human insulin gene in. The segments of specific DNA molecules obtained by recombinant DNA technology can be analysed for determining their nucleotide sequence.
Identify cells containing recombinant plasmid by ability to grow in presence of ampR and tetR 7. Add DNA ligase to bond covalently 5. Recombinant DNA technology leads to genetically modified organisms GMOs.
The vector is then used to carry this foreign genetic information into another cell. Enzymatic method or Sangers Dideoxy method. Cut both DNA with some restriction enzyme 3.
The final plasmid is the combination of the vector original clipped plasmid and the inserted genes. The main steps of the production of recombinant DNA molecules are DNA isolation digestion with restriction enzymes ligation of the gene of interest to the vector and amplifying recombinant DNA molecule inside a host cell. This step uses restriction enzymes and DNA ligase and is called a ligation.
As recombinant DNA technology advances technique precision must be balanced by ethical. There are two fundamental differences between the methods. The restriction endonucleases are sequence-specific typically palindrome sequences and snip the DNA at.
In practice the procedure is carried out by inserting a DNA fragment into a small DNA molecule and then allowing this molecule to. Due to tremendous advancement and broad range of application in the field of recombinant DNA technology this review article mainly focuses on its importance and the. The most common recombinant DNA is the insertion of genes into bacterial plasmids circular DNA that contains all necessary components for the production of the recombinant protein.
Restriction enzyme that can locate and cut the gene from the DNA segment cuts an opening in the recipient DNA usually a plasmid where the donor DNA can be attached. This recombinant micro-organism could now produce the protein encoded by the human gene. Introduce recombinant molecules into bacterial cells.
It is recombinant in the sense that it is composed of DNA from two different sources. Put plasmid into bacterium by transformation 6.

Process Of Recombinant Dna Technology Genetic Engineering Simplebiology Recombinant Dna Dna Technology Genetic Engineering

Recombinant Plasmid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Steps For Recombinant Dna Technology Bacterial Plasmids With A Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment